Polyurethane (PU) resins combine flexibility, strength, biocompatibility, and processability, making them a cornerstone in medical manufacturing. From flexible tubing and catheters to foam wound dressings, device coatings, surgical adhesives, and durable equipment parts, medical-grade PUs enable lightweight, robust, and safe solutions. This article reviews PU chemistry and medical grades, key applications, manufacturing and QA, biocompatibility and sterilization, plus storage and shelf-life best practices.
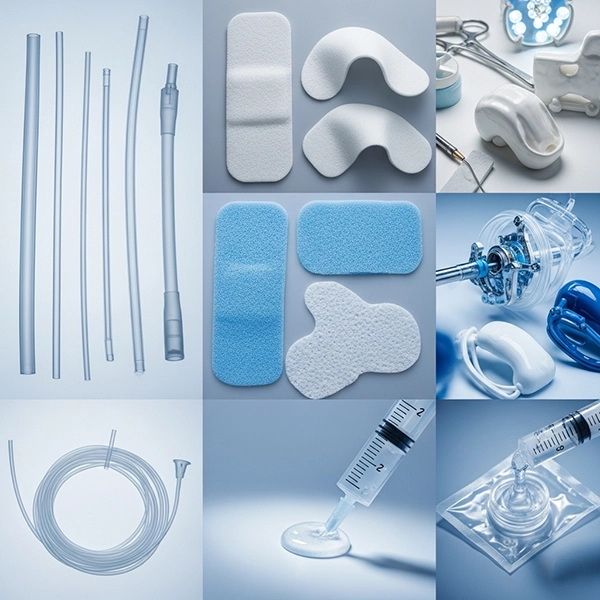

Medical PUs form by reacting isocyanates with polyols. Aliphatic isocyanates (e.g., HDI, H12MDI) are preferred for oxidative and color stability. Polyether, polyester, or polycarbonate polyols are used; polycarbonate urethanes (PCU) are favored for long-term body contact due to superior oxidation and fatigue resistance.
Design note: Select hardness, clarity, radiation/steam stability, chemical resistance (lipids, alcohols), and adhesion to substrates (PVC/nylon) based on end-use and sterilization path.

For long-term implants, PCU grades and thorough biocompatibility/oxidation assessments are essential.
TPUs are extruded/injection-molded; 2K PUs require precise mix ratios, degassing, and controlled curing. Critical controls include viscosity, NCO content, gel time, final Shore hardness, tensile/tear strength, elastic recovery, and optical clarity. Document ISO 10993 biocompatibility, ISO 11135/11137 sterilization validations, and extractables/leachables profiles.
Medical PUs typically tolerate EO, gamma, and e-beam. Aliphatic grades resist radiation-induced yellowing better. Align grade selection with the final sterilization route to avoid property loss.
By combining mechanical performance, safety, and manufacturability, polyurethane resins are ideal for a wide range of medical products. For grade selection guidance, medical supply, or OEM collaboration, visit the Behsou Shafa Medical Polyurethane Products page.